Ever pondered how the seemingly abstract world of mathematics can be visually translated into something tangible and understandable? The answer lies in the x and y graph, a fundamental tool that unlocks the secrets of equations, data, and relationships, making the complex comprehensible.
At its core, an x and y graph, also known as a coordinate graph or Cartesian plane graph, is a visual representation of mathematical relationships. It provides a framework for plotting points, graphing functions, and visualizing equations. This fundamental concept underpins a vast array of disciplines, from basic algebra to advanced calculus, statistics, and beyond. The very essence of this graphing system is the presence of two perpendicular axes, the x-axis (horizontal) and the y-axis (vertical), which intersect at a point called the origin (0, 0).
The same mathematical operations are supported as in the x and y transformation functions, allowing for a wide range of visualizations. This includes the ability to plot functions like A x^2 + bx + c, representing parabolas, or to graph linear equations. Free graphing calculators are readily available, instantly graphing your math problems and allowing for immediate exploration of these concepts. Tools like Mathway offer web-based solutions for simplifying these graphical needs. Moreover, interactive, free online graphing calculators like GeoGebra further enhance the learning experience, providing tools to graph functions, plot data, drag sliders, and much more!
- Hannah Barron Bio Age Husband More Unveiled
- Patty Gardell The Untold Story Of Billy Gardells Wife Family
One of the key benefits of x and y graphs is their ability to represent data visually, transforming abstract numbers into intuitive images. This is particularly useful in fields like statistics, where graphs are used to display and analyze data, making patterns and trends easily recognizable. For instance, plotting statistical data requires a degree of precision, often aided by tools that contain 8 lines per inch to ensure accuracy. In business, graphs are utilized to visualize sales trends, market analysis, and financial performance, providing valuable insights for strategic decision-making.
Graphs can be classified into two types, broadly categorized by their purpose and the type of data they represent. Common types include line graphs, bar charts, scatter plots, and histograms. Each type serves a specific purpose, making the selection of the right graph crucial for effective communication. For example, a line graph is ideal for showing trends over time, while a bar chart excels at comparing different categories. Creating charts and graphs online, using data from sources such as Excel, CSV, or SQL, further expands the accessibility and utility of these tools. Google Sheets, known for its versatility, allows users to create various chart types, including bar charts, histograms, box plots, scatter plots, line graphs, and dot plots, alongside its table functionalities.
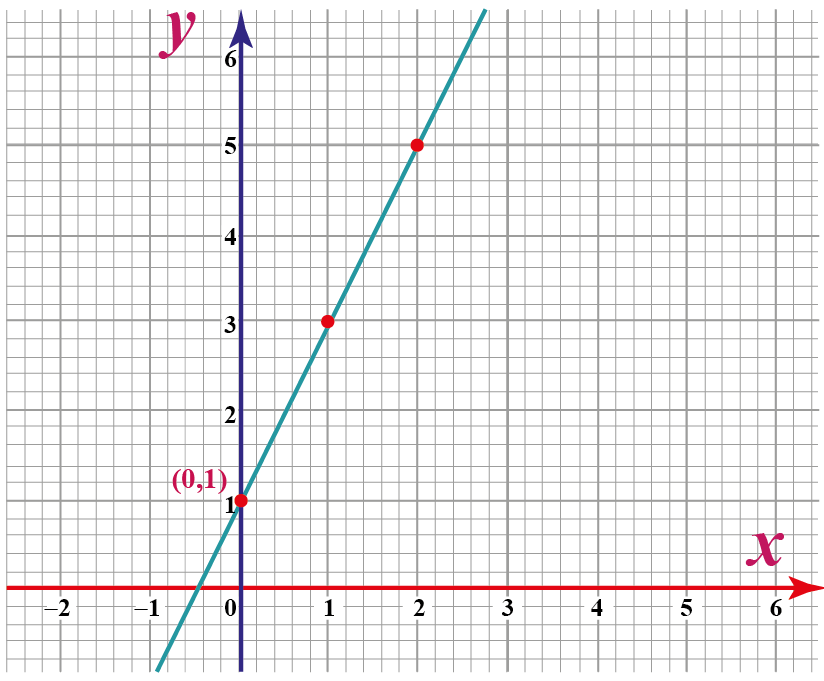
Consider the equation of a line in standard form, where both the [latex]x[\/latex] and [latex]y[\/latex] variables are found on one side of the equation, opposite the constant term. This equation, when graphed, will always cross the y-axis at a specific point when x equals 0. Understanding this behavior is essential when interpreting graphical representations.
- Alice Rosenblum Latest Nude Leaks Onlyfans Content
- Streameast Your Guide To Free Live Sports Alternatives
Explore math with our beautiful, free online graphing calculator. Graph functions, plot points, visualize algebraic equations, add sliders, animate graphs, and more. As you explore these tools, you'll find options to turn on and off any expression by toggling on and off the colored icon to the left of your expression. The ability to pass a function as a parameter, along with the option to pan the graph by holding the shift key and dragging with the mouse, provide enhanced control and flexibility during exploration.
The intersection of the x and y axes forms a grid known as the Cartesian plane or the xy plane. When you graph an expression or equation, you will notice points of interest in gray on your graph. Graphing another function, like \\(g(x)=x^2+1\\), will show the points of intersection of the two curves, providing a visual representation of the solution to the system of equations.
In fact, this is a special case, and we use a different equation, not y=., but instead we use x=. Every point on the line has x coordinate 1.5, that is why its equation is x = 1.5. Coordinate axes and coordinate planes in 3d. In the first quadrant, you can see the x and y coordinates as positive. In the second quadrant, you can see that the \u201cx\u201d coordinate is negative and the \u201cy\u201d coordinate is positive.
The x and y graph is more than just a set of intersecting lines; It holds some distinctive properties. One of the primary features is its division into four sections or quadrants. In quadrant i, both x and y values are positive. In quadrant ii, x takes a negative turn, and y remains positive. There are two graphs here: The horizontal axis x is the same. But, we have two different y axis. Go to the insert tab. An empty graph will be displayed. Give your graph a title. Select the series of your
This leads to the following strategy for choosing the most convenient method to graph a line. The horizontal axis x is the same. But, we have two different y axis. Visit mathway on the web.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | A visual representation of mathematical relationships using two perpendicular axes: the x-axis (horizontal) and the y-axis (vertical). |
| Purpose | To plot points, graph functions, visualize equations, and analyze data. It transforms abstract numbers into easily understandable images, aiding in pattern recognition and analysis. |
| Key Components | X-axis (horizontal), Y-axis (vertical), Origin (0,0), Quadrants (I, II, III, IV), Coordinate points (x, y). |
| Types of Graphs | Line graphs, bar charts, scatter plots, histograms, pie charts, and more. The choice depends on the data and the intended message. |
| Mathematical Operations | Supports various mathematical operations, allowing the graphing of functions like A x^2 + bx + c and solving equations. |
| Applications | Widely used in mathematics, statistics, science, engineering, business (for data visualization), and many other fields. |
| Tools | Free graphing calculators (like Mathway, GeoGebra), spreadsheets (Excel, Google Sheets), and specialized software. |
| Quadrants | The x and y axes divide the plane into four quadrants. Quadrant I: x and y positive; Quadrant II: x negative, y positive; Quadrant III: x and y negative; Quadrant IV: x positive, y negative. |
| Equations | Equations of lines, parabolas, and other functions are easily visualized. For example, the standard form of a line, a x + by = c. |
| Coordinate System | The Cartesian coordinate system provides a unique location for each point in the plane. Each point is represented by an ordered pair (x, y). |
This table demonstrates the breadth of uses for this tool. From the visualization of simple equations to the analysis of complex datasets, the x and y graph remains a cornerstone in countless fields. Its ability to translate mathematical concepts into visual forms makes it an invaluable asset for understanding, analyzing, and communicating complex information.
The x and y graph is more than just a set of intersecting lines; it holds some distinctive properties. One of the primary features is its division into four sections or quadrants. In quadrant I, both x and y values are positive. In quadrant II, x takes a negative turn, and y remains positive. This division allows for precise location and description of points in the coordinate plane. Every point on the line has x coordinate 1.5, that is why its equation is x = 1.5.
Explore math with our beautiful, free online graphing calculator. Graph functions, plot points, visualize algebraic equations, add sliders, animate graphs, and more. You can turn on and off any expression by toggling on and off the colored icon to the left of your expression. The power of these visual tools is in their ability to bridge the gap between abstract theory and concrete understanding. The use of x and y graphs also provides a clear, intuitive approach to many otherwise complex mathematical problems, providing a foundation for further exploration.
- Alex Eubank Height Weight Stats Age Fitness Journey
- Britt Michael Are They Still Together Plus More Updates